How does it act?

Page 1 of 3
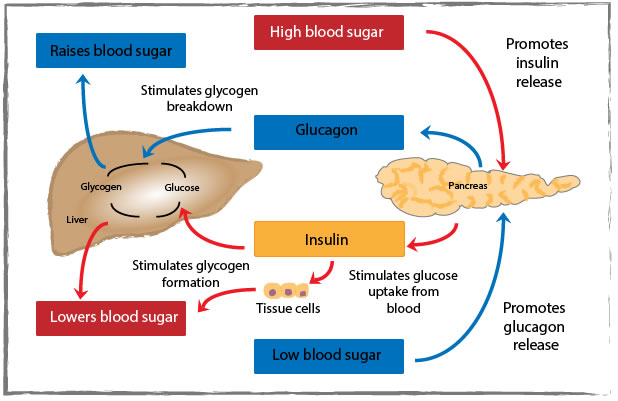
Image adapted from ATrain Education, Inc, USA, 2014.
Insulin is a powerful hormone that acts to reduce blood glucose concentrations. It is released from the pancreatic β cells (Islets of Langerhans) during and after feeding, allowing it to work at just the right time when glucose levels are increased. Insulin release is stimulated by high glucose concentrations. Insulin is stored inside vesicles inside the β cells and when blood glucose concentrations increase, glucose is transported into the β cell by GLUT 2, where it initiates a intracellular signalling cascade, resulting in the movement of the
