How the body decreases blood glucose concentrations

Page 4 of 5
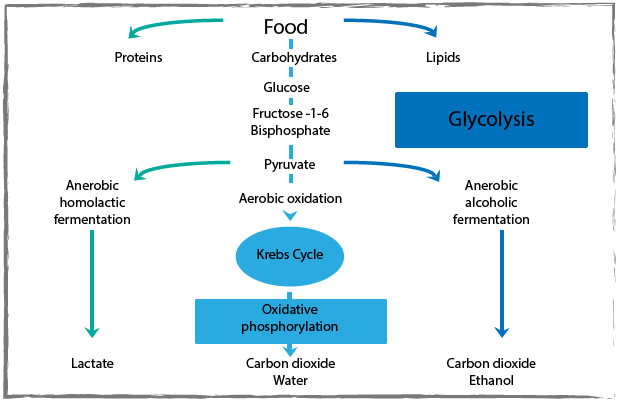
Dr Nicola A. Englyst, Faculty of Medicine, University of Southampton. Used with permission.
Metabolism of glucose to make ATP by glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle
Glucose enters cells where it undergoes phosphorylation to form glucose-6-phosphate. Changing the form that the glucose is in means that glucose cannot be transported back outside the cell, and the cells sense that the concentration of glucose is higher outside the cell than inside. Therefore they keep transporting glucose into the cells, resulting in a reduction in glucose concentrations in the bloodstream.

