How the body decreases blood glucose concentrations

Page 2 of 5
Professor Rohan Lewis, Faculty of Medicine, University of Southampton. Used with permission.
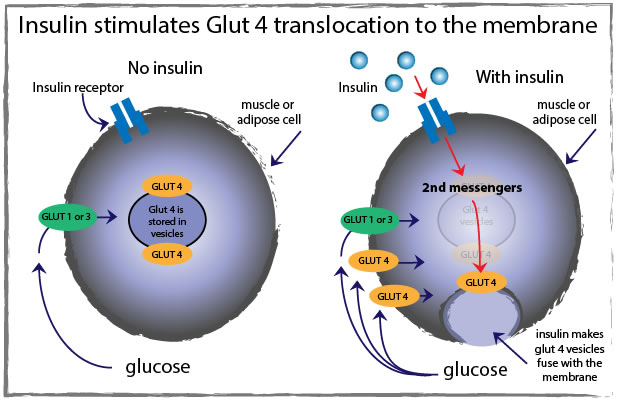
GLUT 1 and 3 provide basal glucose uptake, meaning the cell always has the capability to take up low levels of glucose. However, GLUT 4 is insulin-sensitive (muscle or adipose cells). This means that when we eat, glucose upregulates insulin, and insulin binding to the insulin receptor results in the movement of GLUT 4 from intracellular granules to the cell membrane, enabling uptake of large amounts of glucose by cells. Therefore, glucose is removed from the blood stream and enters cells.

